My TDD Journey Started Dec 6, 1999
My story of learning Test-Driven Development started 23 years ago today. TDD has helped me exercise my code well before there is target hardware to run on. TDD helps me prevent defects. It can help you too.

More than just a pretty face - a good UI is essential
A user interface can make or break a device - determining its success in the marketplace. With careful design, the UI can make the product compelling and result in a high level of satisfaction from new and experienced users.

Lightweight C++ Error-Codes Handling
The traditional C++ approach to error handling tends to distinguish the happy path from the unhappy path. This makes handling errors hard (or at least boring) to write and hard to read. In this post, I present a technique based on chaining operations that merges the happy and the unhappy paths. Thanks to C++ template and inlining the proposed technique is lightweight and can be used proficiently for embedded software.

Embedded Systems Roadmaps
What skills should every embedded systems engineer have? What should you study next to improve yourself as an embedded systems engineer? In this article I'll share with you a few lists from well-respected sources that seek to answer these questions, with the hope of helping provide you a path to mastery. Whether you've only just finished your first Arduino project or you've been building embedded systems for decades, I believe there's something in here for everyone to help improve themselves as embedded systems engineers.
Embedded Systems Co-design for Object Recognition: A Synergistic Approach
Embedded systems co-design for object recognition is essential for real-time image analysis and environmental sensing across various sectors. This methodology harmonizes hardware and software to optimize efficiency and performance. It relies on hardware accelerators, customized neural network architectures, memory hierarchy optimization, and power management to achieve benefits like enhanced performance, lower latency, energy efficiency, real-time responsiveness, and resource optimization. While challenges exist, co-designed systems find applications in consumer electronics, smart cameras, industrial automation, healthcare, and autonomous vehicles, revolutionizing these industries. As technology advances, co-design will continue to shape the future of intelligent embedded systems, making the world safer and more efficient.

What is Pulse Width Modulation and How Does It Work?
Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) is a technique used to control the average voltage supplied to a device or component by adjusting the width of a series of pulses. It works by rapidly turning a signal on and off at a specific frequency. The crucial element of PWM is the duty cycle, which represents the percentage of time the signal is “on” (high voltage) compared to the total time of one cycle.

Getting Started With Zephyr: Saving Data To Files
In this blog post, I show how to implement a Zephyr application to mount a microSD card, create a new file on the microSD card, and write data to it. The lessons learned from such an application can be helpful for devices out in the field that need to write data to off-board memory periodically, especially in cases where Internet access may be sporadic.

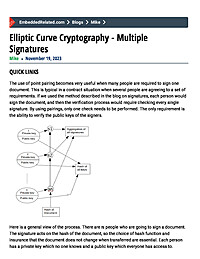
Elliptic Curve Cryptography - Extension Fields
An introduction to the pairing of points on elliptic curves. Point pairing normally requires curves over an extension field because the structure of an elliptic curve has two independent sets of points if it is large enough. The rules of pairings are described in a general way to show they can be useful for verification purposes.

How to Implement Image Processing Algorithms in FPGA Hardware
Recognized for their parallelism and reconfigurability, FPGAs prove ideal for real-time processing in medical imaging and computer vision. The step-by-step approach starts with understanding FPGA basics, emphasizing their reconfigurable nature and parallel processing. It guides users in algorithm selection based on factors like processing speed, resource utilization, and adaptability, then highlights designing modular and scalable algorithms. The process includes simulation for verification, synthesis using tools like Xilinx Vivado and Intel Quartus Prime, interfacing with image sensors, and testing on real hardware. The conclusion underscores FPGA's advantages in image processing, presenting ongoing opportunities for innovation in diverse industries.

Modern C++ in Embedded Development: (Don't Fear) The ++
While C is still the language of choice for embedded development, the adoption of C++ has grown steadily. Yet, reservations about dynamic memory allocation and fears of unnecessary code bloat have kept many in the C camp. This discourse aims to explore the intricacies of employing C++ in embedded systems, negotiating the issues of dynamic memory allocation, and exploiting the benefits of C++ offerings like std::array and constexpr. Moreover, it ventures into the details of the zero-overhead principle and the nuanced distinctions between C and C++. The takeaway? Armed with the right knowledge and a careful approach, C++ can indeed serve as a powerful, safer, and more efficient tool for embedded development.

C++ on microcontrollers 1 - introduction, and an output pin class
This blog series is about the use of C++ for modern microcontrollers. My plan is to show the gradual development of a basic I/O library. I will introduce the object-oriented C++ features that are used step by step, to provide a...

MSP430 LaunchPad Tutorial - Part 4 - UART Transmission
Today we are going to learn how to communicate using UART with the Launchpad. For this purpose I will replace the default microcontroller that comes with the board with the MSP430G2553. It is the most powerful device in the MSP430 Value Line and...

Square root in fixed point VHDL
We will design and implement a fixed point square root function in VHDL. The algorithm is based on the recursive inverse square root algorithm based on Newton Raphson and offers parametrizable pipeline depth, word length and the algorithm is built on records and procedures.

C to C++: Using Abstract Interfaces to Create Hardware Abstraction Layers (HAL)
In C to C++, we've been exploring how to transition from a C developer to a C++ developer when working in embedded system. In this post, we will explore how to leverage classes to create hardware abstraction layers (HAL). You'll learn about the various inheritance mechanisms, what an virtual function is, and how to create an abstract class.

Review: Hands-On RTOS with Microcontrollers
Full disclosure: I was given a free copy of this book for evaluation.Hands-On RTOS with Microcontrollers: Building real-time embedded systems using FreeRTOS, STM32 MCUs, and SEGGER debug tools by Brian Amos is an outstanding book. It lives...

Boot sequence for an ARM based embedded system -2
In the last post, we discussed about the startup execution sequence on an ARM based embedded system in broader terms. In this post, we are going to cover the details of a startup code.These details are also available through various ARM resources...

Getting Started with the Microchip PIC® Microcontroller
This first post of a five part series looks at the available hardware options for getting started with Microchip 8-bit PIC® Microcontroller, explores the MPLAB® X Integrated Development Environment and walks through setting up a project to expose the configured clock to an external pin and implement a single output GPIO to light an LED.
How Embedded Linux is used in Spacecrafts !
This article dives into the application of Linux in spacecraft, examining the challenges it poses and proposing potential solutions. Real-life examples will be discussed, while also addressing the drawbacks of employing Linux in safety-critical missions.