
An Engineer's Guide to the LPC2100 Series
This book is intended as a hands-on guide for anyone planning to use the Philips LPC2000 family of microcontrollers in a new design. It is laid out both as a reference book and as a tutorial. It is assumed that you have some experience in programming microcontrollers for embedded systems and are familiar with the C language. The bulk of technical information is spread over the first four chapters, which should be read in order if you are completely new to the LPC2000 and the ARM7 CPU.

Choosing An Ultralow-Power MCU
This application report describes how to compare ultralow-power MCUs. It discusses the key differences between popular low-power MCUs and how to interpret features and specifications and apply them to application requirements
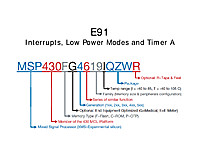
Interrupts, Low Power Modes and Timer A
This document contains a lot of what you need to know to get the most out of the MSP430. The MSP430 line is renowned for it's low power usage, and to really utilize it well you have to architect your software to be an interrupt driven device that utilizes the low power modes.

PID Without a PhD
PID (proportional, integral, derivative) control is not as complicated as it sounds. Follow these simple implementation steps for quick results.
Reed-Solomon Error Correction
[Best paper on Reed-Solomon error correction I have ever read -- and it's from the BBC!] Reed-Solomon error correction has several applications in broadcasting,in particular forming part of the specification for the ETSI digital terrestrial television standard, known as DVB-T. Hardware implementations of coders and decoders for Reed-Solomon error correction are complicated and require some knowledge of the theory of Galois fields on which they are based. This note describes the underlying mathematics and the algorithms used for coding and decoding,with particular emphasis on their realisation in logic circuits. Worked examples are provided to illustrate the processes involved.
Memory allocation in C
This article is about dynamic memory allocation in C in the context of embedded programming. It describes the process of dynamically allocating memory with visual aids. The article concludes with a practical data communications switch example which includes a sample code in C.

Red Hat Linux - The Complete Reference
This book identifies seven major Linux topics: basic setup, environments and applications, the Internet, servers, administration, and network administration. These topics are integrated into the different ways Red Hat presents its distribution: as a desktop workstation, network workstation, server, and development platform

Essential Linux Device Drivers
This book is about writing Linux device drivers. It covers the design and development of major device classes supported by the kernel, including those I missed during my Linux-on-Watch days. The discussion of each driver family starts by looking at the corresponding technology, moves on to develop a practical example, and ends by looking at relevant kernel source files. Before foraying into the world of device drivers, however, this book introduces you to the kernel and discusses the important features of 2.6 Linux, emphasizing those portions that are of special interest to device driver writers.

CPU Memory - What Every Programmer Should Know About Memory
As CPU cores become both faster and more numerous, the limiting factor for most programs is now, and will be for some time, memory access. Hardware designers have come up with ever more sophisticated memory handling and acceleration techniques–such as CPU caches–but these cannot work optimally without some help from the programmer. Unfortunately, neither the structure nor the cost of using the memory subsystem of a computer or the caches on CPUs is well understood by most programmers. This paper explains the structure of memory subsystems in use on modern commodity hardware, illustrating why CPU caches were developed, how they work, and what programs should do to achieve optimal performance by utilizing them.

PID Without a PhD
PID (proportional, integral, derivative) control is not as complicated as it sounds. Follow these simple implementation steps for quick results.

Time in Wireless Embedded System
Wireless embedded networks have matured beyond academic research as industry now considers the advantages of using wireless sensors. With this growth, reliability and real-time demands increase, thus timing becomes more and more relevant. In this dissertation, we focus on the development of highly stable, low-power clock systems for wireless embedded systems. Wireless embedded networks, due to their wire-free nature, present one of the most extreme power budget design challenges in the field of electronics. Improvements in timing can reduce the energy required to operate an embedded network. However, the more accurate a time source is, the more power it consumes. To comprehensively address the time and power problems in wireless embedded systems, this dissertation studies the exploitation of dual-crystal clock architectures to combat effects of temperature induced frequency error and high power consumption of high-frequency clocks. Combining these architectures with the inherent communication capabilities of wireless embedded systems, this dissertation proposes two new technologies; (1) a new time synchronization service that automatically calibrates a local clock to changes in temperature; (2) a high-low frequency timer that allows a duty-cycled embedded system to achieve ultra low-power sleep, while keeping fine granularity time resolution offered only by high power, high frequency clocks.

Enhanced Sample Rate Mode Measurement Precision
The low-noise system architecture and the tailored frequency response employed in the HDO4000A, HDO6000A, HDO8000A and MDA800A series provides the foundation for enhancing ADC sample rates through additional techniques. In this case, carefully constructed filters combined with a pristine front-end amplifier and a frequency response carefully limited to 1 GHz provide the opportunity to provide more measurement precision than would otherwise be possible. The technique utilized to achieve higher measurement precision is interpolation, and this technique is used by default as an Enhanced Sample Rate up to 10 GS/s. By integrating the Enhanced Sample Rate functionality with the normal Timebase controls for Sample Rate, Time and Acquisition Memory adjustment, the oscilloscopes are optimized for best waveform signal fidelity in all situations.
What’s a Multicore Microcontroller?
This tutorial answers the question “What’s a multicore microcontroller?”
Electrical Ground Rules Part 3
Best Practices for Grounding Your Electrical Equipment Examining the role of ground as a voltage stabilizer and transient limiter, along with tips on improving safety and signal integrity (Part 3 of 3)
Electrical Ground Rules Part 2
Best Practices for Grounding Your Electrical Equipment Examining our use of ground as protection, and how ground fault circuit interrupter devices operate to protect us from severe shock (Part 2 of 3)

Essential Linux Device Drivers
This book is about writing Linux device drivers. It covers the design and development of major device classes supported by the kernel, including those I missed during my Linux-on-Watch days. The discussion of each driver family starts by looking at the corresponding technology, moves on to develop a practical example, and ends by looking at relevant kernel source files. Before foraying into the world of device drivers, however, this book introduces you to the kernel and discusses the important features of 2.6 Linux, emphasizing those portions that are of special interest to device driver writers.

Introduction to Embedded Systems
This is the first chapter in the book Embedded Systems Hardware for Software Engineers.

Driving I2C-Bus Signals Over Twisted Pair Cables with PCA9605
The availability of powerful I2C buffers that drive their I/Os on both sides to a nominal ground or ‘zero offset’ logic level allows the removal of noise introduced into one section of a larger bus system. That ‘regeneration’ of clean I2C signals enables building long I2C buses by combining together relatively short bus sections, each say less than 20 meters, using such buffers or multiplexers that contain them. Conventional twisted pair communication cabling with its convenient connectors, and a ‘modular’ I2C system approach, make large system assembly easy. Each drop point or node can be individually selected for bidirectional data communication with the Master just by using normal I2C software addressing. As an example, a system is described for control of LED lighting displays and it is suggested that the power for the LEDs, and the I2C control system, might be economically provided using ‘extra low voltage’ distribution at 48 V using either the control signal cable or similar low cost wiring in a manner similar to that used in ‘Power over the Ethernet’ systems. The simplicity and flexibility of this approach makes it attractive to consider as an alternative to other control systems such as RS-485 or CAN bus.
Arduino Programming Notebook
This notebook serves as a convenient, easy to use programming reference for the command structure and basic syntax of the Arduino microcontroller. To keep it simple, certain exclusions were made that make this a beginner’s reference best used as a secondary source alongside other websites, books, workshops, or classes. This decision has lead to a slight emphasis on using the Arduino for standalone purposes and, for example, excludes the more complex uses of arrays or advanced forms of serial communication.



















